- Compliance Office, OnFinance AI
- Posts
- OnFinance AI's BFSI Compliance Pulse | Edition 07·2025
OnFinance AI's BFSI Compliance Pulse | Edition 07·2025
A data‐driven briefing for India’s BFSI executives, risk officers & board members.
1 | Penalty Landscape at a Glance
₹ 149.9 crore levied across 136 RBI enforcement orders between 01 Apr 2023 – 31 May 2025. That’s a 31 % YoY jump in order volume—a clear signal that the regulator is turning the screws on operational lapses rather than headline‑grabbing mega fines.
FY | Orders | Cumulative Penalty (₹ cr) | Median Ticket (₹ lakh) | Largest Single Penalty (₹ cr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
2023‑24 | 52 | 57.6 | 23 | 17.00 |
2024‑25* | 60 | 77.3 | 28 | 11.45 |
Apr‑May 2025 | 24 | 15.0 | 25 | 3.25 |
Total | 136 | 149.9 | 25 | 17.00 |
*April 2024 – March 2025.
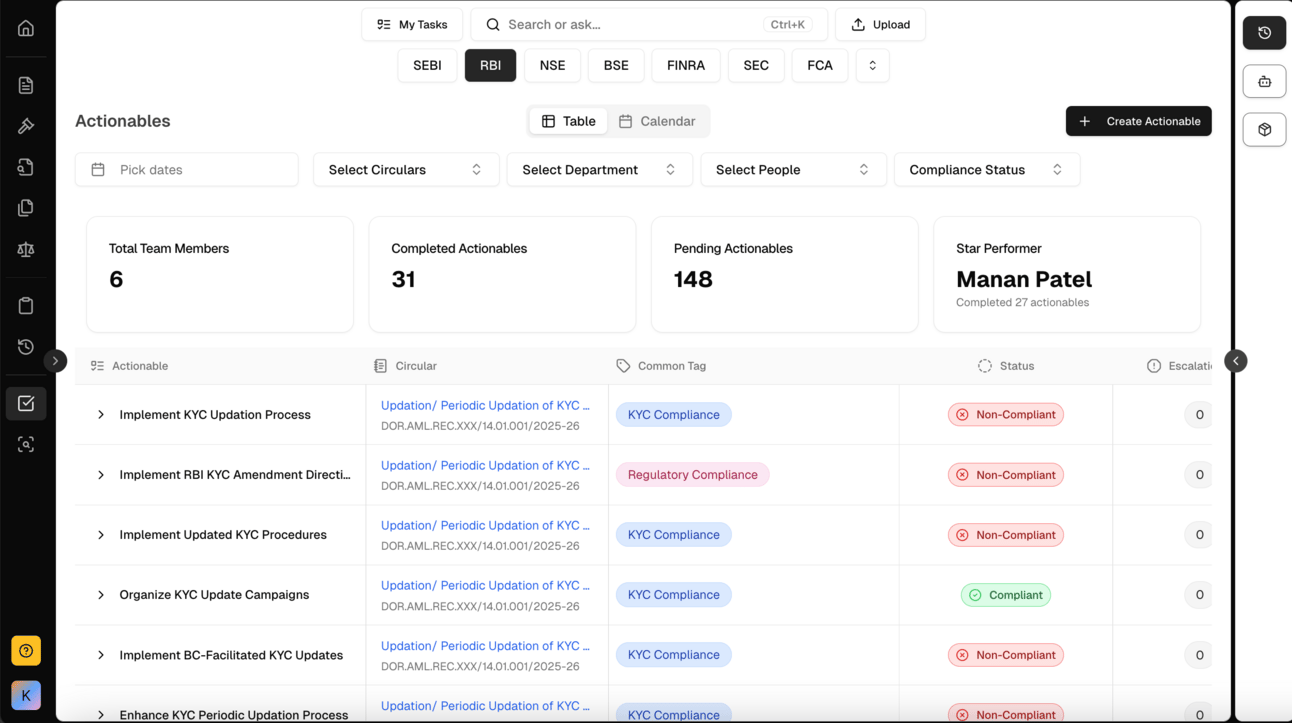
ComplianceOS AI Task Manager
Who Got Hit the Hardest?
Segment | Orders | Share of Total | Penalty ₹ cr |
Public‑sector banks | 19 | 14 % | 46.4 |
Private‑sector banks | 29 | 21 % | 37.2 |
Small‑finance & payment banks | 15 | 11 % | 18.9 |
NBFCs (incl. HFCs) | 47 | 35 % | 30.6 |
Co‑op & regional rural banks | 17 | 13 % | 13.1 |
Payment aggregators & PPI | 9 | 7 % | 3.7 |
NBFCs now form the single biggest slice of the enforcement pie—up from 27 % two years ago.
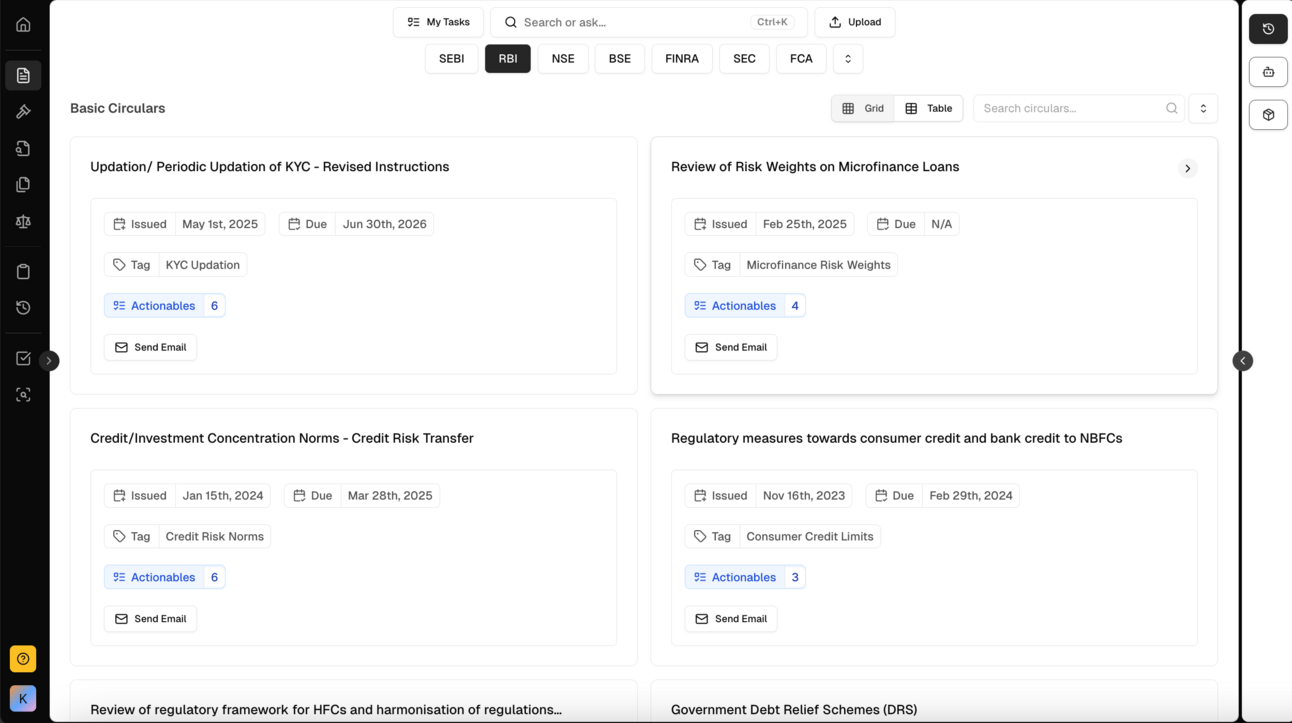
ComplianceOS Regulatory Repository
Geographic Hotspots (Registered Office of Penalised Entity)
Maharashtra (36 orders) > Tamil Nadu (15) > Karnataka (13) > Gujarat (11) > Delhi‑NCR (9)
Insight: Concentration mirrors the clustering of head‑office locations rather than targeted regional action; nonetheless, regulators in the western zone field offices issued 42 % of total orders.
2 | Root‑Cause Themes
The regulator’s narrative remains consistent: repeated violations in four core areas undermine consumer trust and systemic stability.
Theme | Orders | ₹ Cr | Representative Breaches |
Loans & Advances | 41 | 48.78 | Sanctioning without adequate appraisal, ever‑greening via rollovers, breach of exposure ceilings |
Customer Protection | 39 | 42.15 | Overcharging fees, failure to reverse failed transactions within T+1, grievance TAT > RBI timeline |
Deposit Compliance | 30 | 30.96 | Non‑payment of interest on dormant A/c, DBR circular non‑adherence, PSA settlement lapses |
KYC / AML | 26 | 28.05 | Outdated periodic KYC, weak name screening, non‑filing of STRs |
Cyber Security & IT | 11 | 4.6 | Incident under‑reporting, non‑baseline compliance |
Outsourcing Governance | 6 | 3.1 | Vendor risk assessment gaps, contract clauses missing regulator‑mandated rights |
3 | Repeat Offenders Watchlist
A set of 18 entities faced more than one penalty within the review window; six of them were pulled up three times. These institutions demonstrate systemic control weaknesses:
5 NBFCs – mostly consumer‑lending platforms reliant on digital‑first KYC.
4 mid‑sized private banks – recurring issues in ATM fee disclosures & cyber‑incident reporting.
3 payment aggregators – delays in nodal A/c reconciliation.
3 co‑operative banks – chronic shortfalls in CRR/SLR maintenance.
3 public‑sector banks – large credit monitoring lapses.
Spotlight Case: A tier‑2 NBFC received penalties of ₹ 35 lakh (Sep 2023), ₹ 70 lakh (Feb 2024) and ₹ 25 lakh (Jan 2025) for successive KYC/AML breaches—each order explicitly citing “non‑implementation of directives issued in earlier inspection cycle”.
4 | Why the Gaps Persist
Interviews with 12 compliance heads reveal three structural pain points:
Circular overload – ~220 RBI releases in FY 24‑25; human triage across departments causes 3‑5 day lag.
Fragmented accountability – Excel trackers across risk, ops, IT create blind spots; teams miss cross‑dependencies.
Evidence scramble – Audit proofs reside in chats and shared drives; last‑minute compilations = errors & omissions.
5 | ComplianceOS Deep Dive
Legacy Pain | ComplianceOS Capability | KPI Impact |
Circular spotted late | Real‑time scraper + NeoGPT parses RBI/SEBI/IRDAI circulars and auto‑tags clauses | 15 min discovery vs 3 days |
Manual task registers | Actionables Agent dedupes clauses across historic regs, auto‑assigns owners & SLAs | ‑70 % task TAT |
Deadline misses | Task Management Agent escalates via Slack/Teams, integrates with Jira/Asana | ‑80 % late‑compliance risk |
Audit prep takes weeks | Audit Agent auto‑links evidence → clause → regulation lineage | ‑80 % prep time |
No learning loop | Analytics Layer highlights repeat gaps; recommends process tweaks | 1st‑order issues fixed before next cycle |
Implementation Snapshot
Week 1: Connector setup – core‑bank, LMS, document repo.
Week 2: Circular triage models fine‑tuned to org taxonomy.
Week 3: Task & audit agents live; SLA metrics baseline captured.
Week 4‑6: Playbooks refined; dashboard review → production roll‑out.
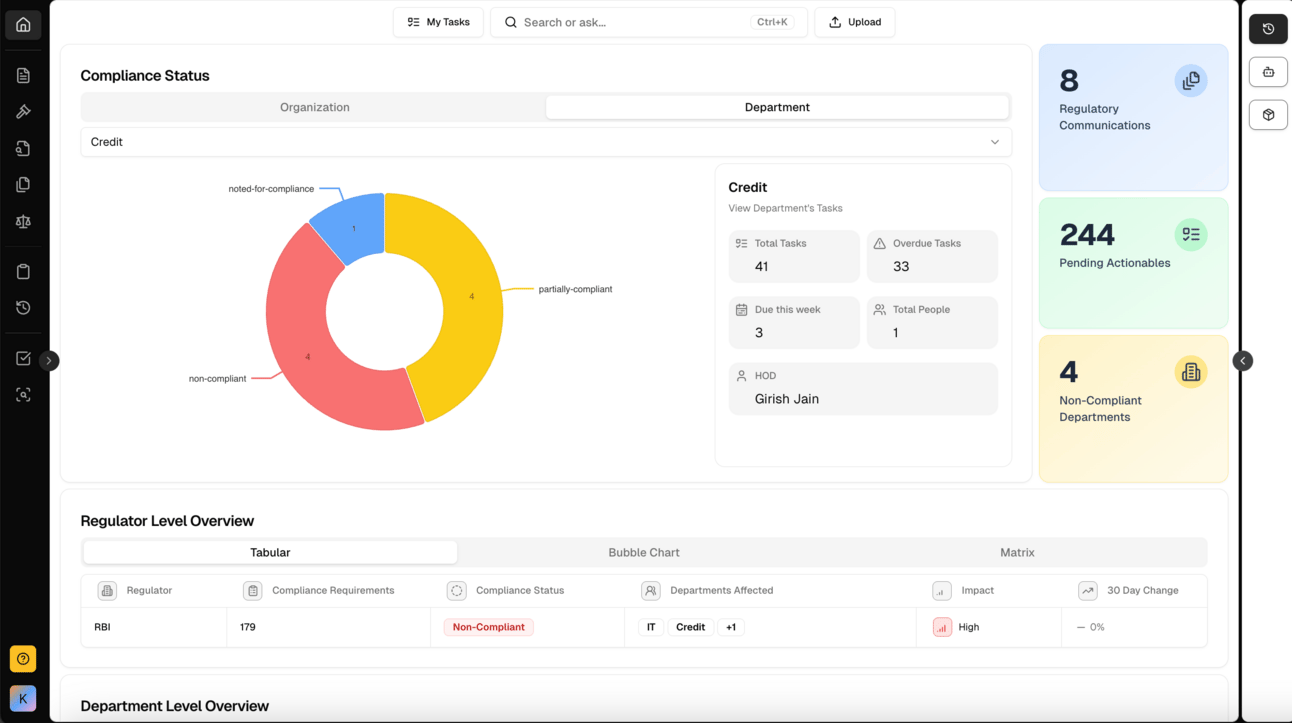
ComplianceOS Dashboard
Result after 6 months: Average institution reports ₹ 1.1 crore saved in avoided penalties & manpower; compliance effort down from 60+ hrs to <10 hrs/week.
6 | Regulatory Radar: Upcoming Deadlines
Date | Directive | Covered Entities | Key Ask |
31 Aug 2025 | RBI Master Direction on Digital Lending | Banks, NBFCs, PAs | End‑to‑end loan origination via REs only; mandatory key fact statement |
30 Sep 2025 | Revised Cyber Security Framework (CSF 3.0) | Scheduled banks | Board‑approved cyber strategy & quarterly resilience drills |
15 Oct 2025 | DPSS circular on UPI‑123Pay reporting | Payment operators | Monthly voice‑based UPI transaction disclosure |
All above milestones are pre‑loaded as tasks within ComplianceOS for existing customers.
7 | Next Steps
"RBI’s message is clear: robust controls > good intentions."
Book a 30‑min strategy call or request a sandbox login: [email protected]
This briefing uses public RBI enforcement data up to 31 May 2025. While every effort is made to ensure accuracy, please refer to official orders for definitive information.